Voyaging the Cosmos: A Fascinating World of Cosmic Probes
To unlock the secrets of Infinite Consciousness, it's evident that exploring space is crucial. Some grasp this profound awareness by studying nature and space, while others rely on Cosmic probes as indispensable allies to journey through the cosmos and relay information back to Earth. Throughout history, space exploration has thrived, and remarkable probes have emerged. These masterful creations have been invaluable in understanding neighboring planets and worlds, earning their place in history for their groundbreaking achievements and unwavering friendship with humanity.
Credit for Videos on Link goes to NASA and other owned sources
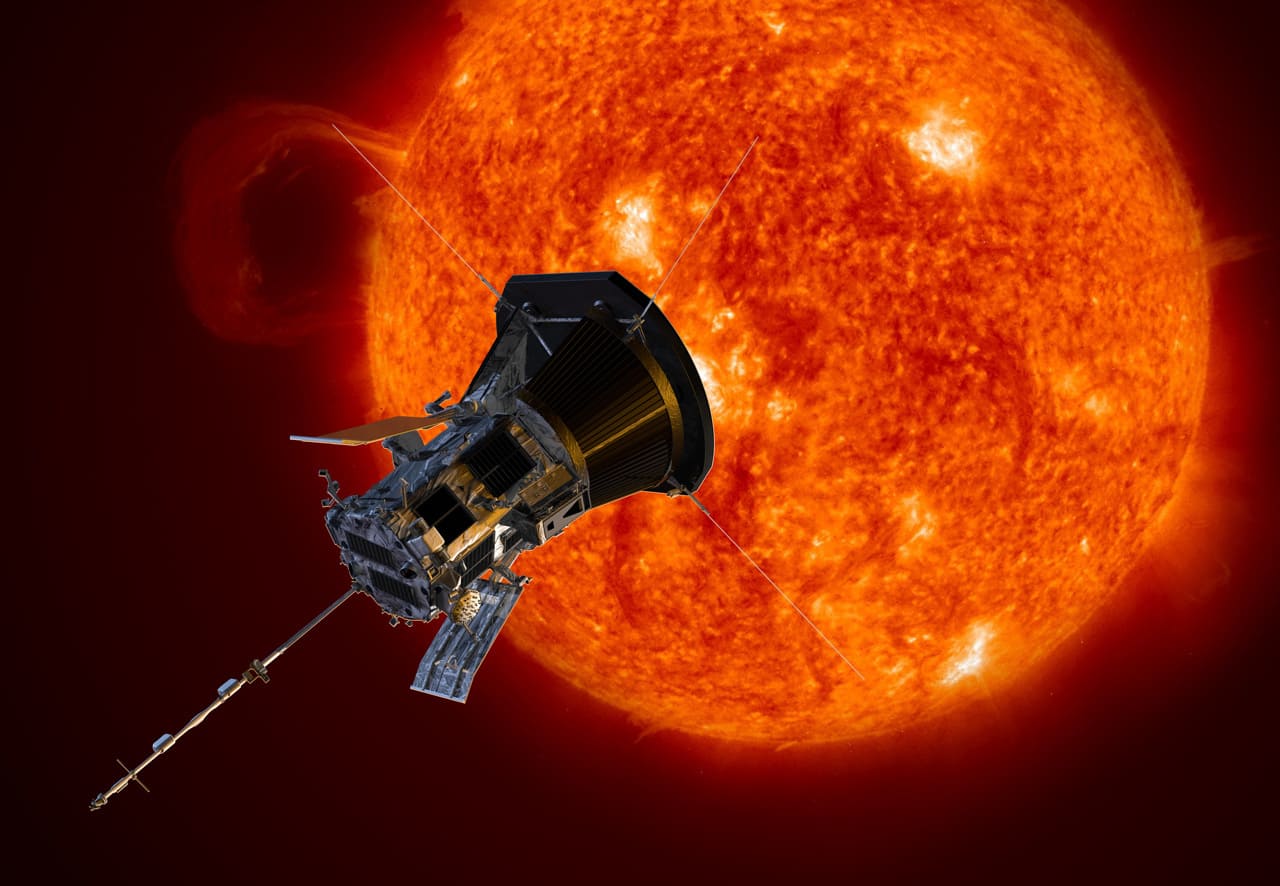
Parker Solar Probe
A scientific mission to unlock the mysteries of the Sun's corona and solar wind A spacecraft that uses breakthrough technology and autonomy to endure heat and radiation like no other mission A unique solar observatory that will orbit within 4 million miles of our star's surface to directly study the formation of the solar wind The first mission named for a living scientist: Dr. Eugene Parker, who theorized the existence of the solar wind
Click to watch Parker Solar Probe Launch!!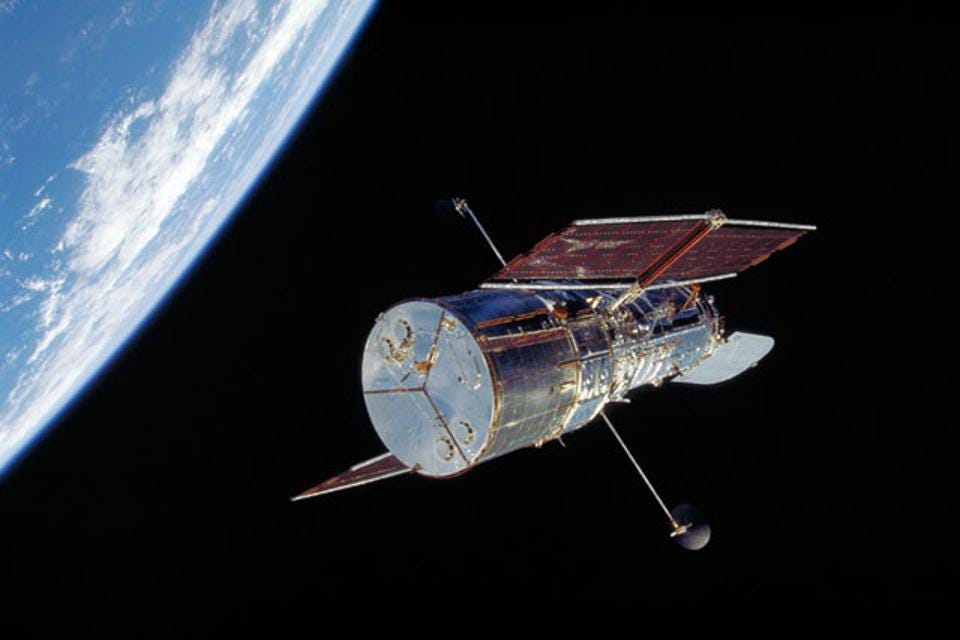
Hubble Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the first sophisticated optical observatory placed into orbit around Earth. Earth’s atmosphere obscures ground-based astronomers’ view of celestial objects by absorbing or distorting light rays from them. A telescope stationed in outer space is entirely above the atmosphere, however, and receives images of much greater brightness, clarity, and detail than do ground-based telescopes with comparable optics.
Click to watch Hubble Space Telescope lauch!!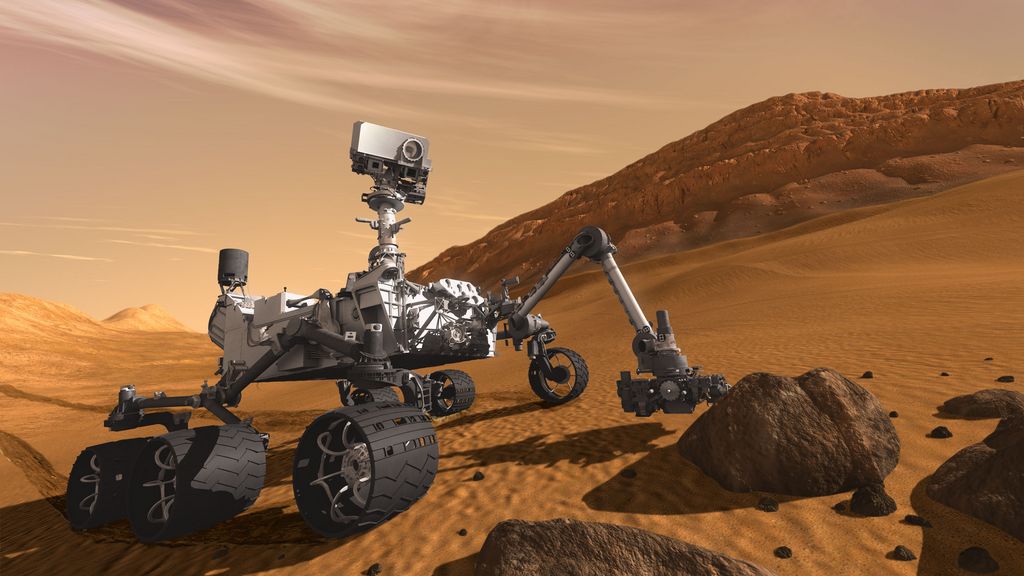
Curiosity Rover
The Mars Science Laboratory and its rover centerpiece, Curiosity, is the most ambitious Mars mission yet flown by NASA. The rover landed on Mars in 2012 with a primary mission to find out if Mars is, or was, suitable for life. Another objective is to learn more about the Red Planet's environment. In March 2018, it celebrated 2,000 sols (Mars days) on the planet, making its way from Gale Crater to Aeolis Mons (colloquially called Mount Sharp), where it has looked at geological information embedded in the mountain's layers. Along the way, it also has found extensive evidence of past water and geological change.
Click to watch Animated deployment of Curiosity on Mars!!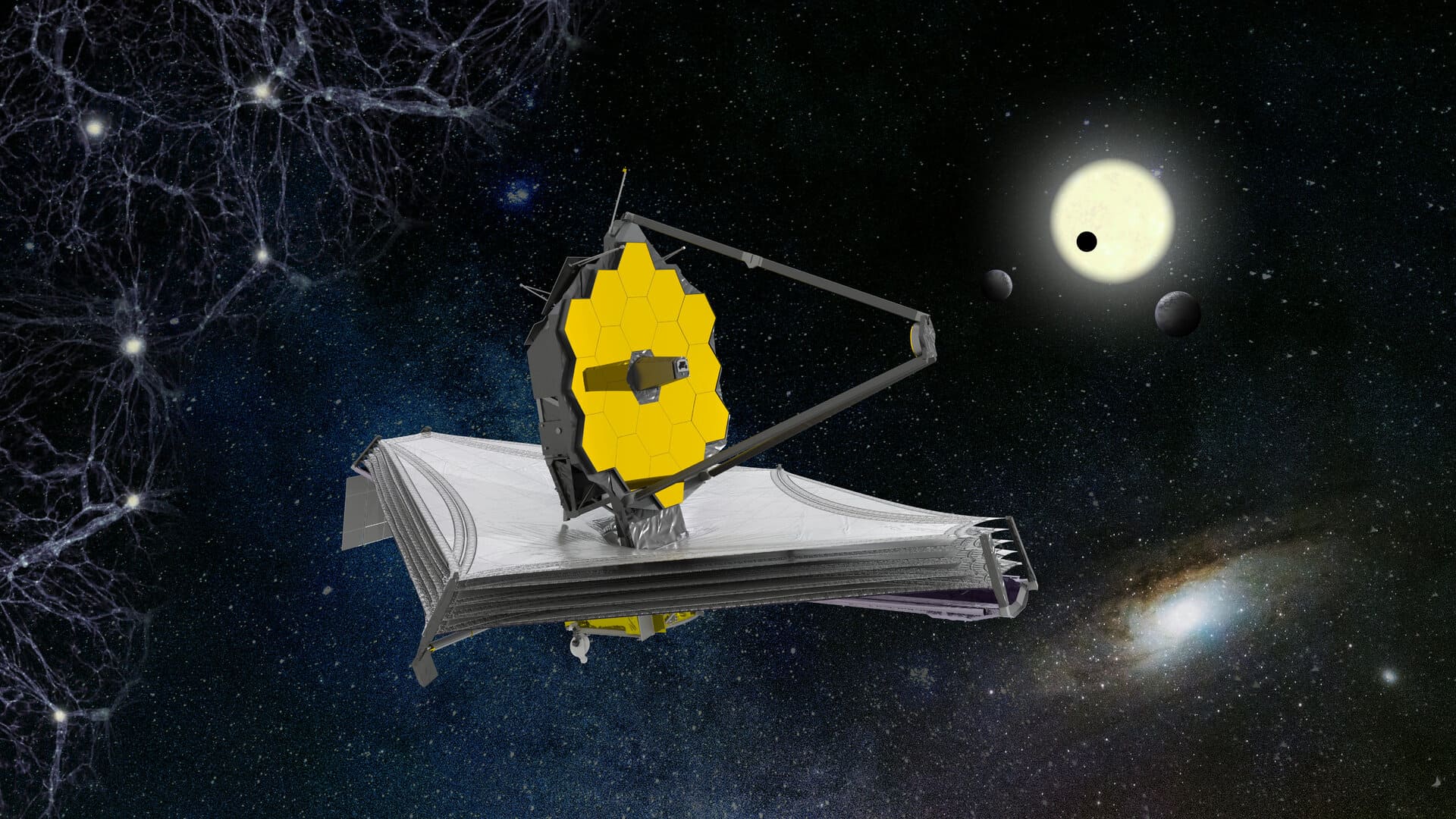
James Webb Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed primarily to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its greatly improved infrared resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too early, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This is expected to enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the first stars and the formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.
Click to watch The James Webb telescope Launch!!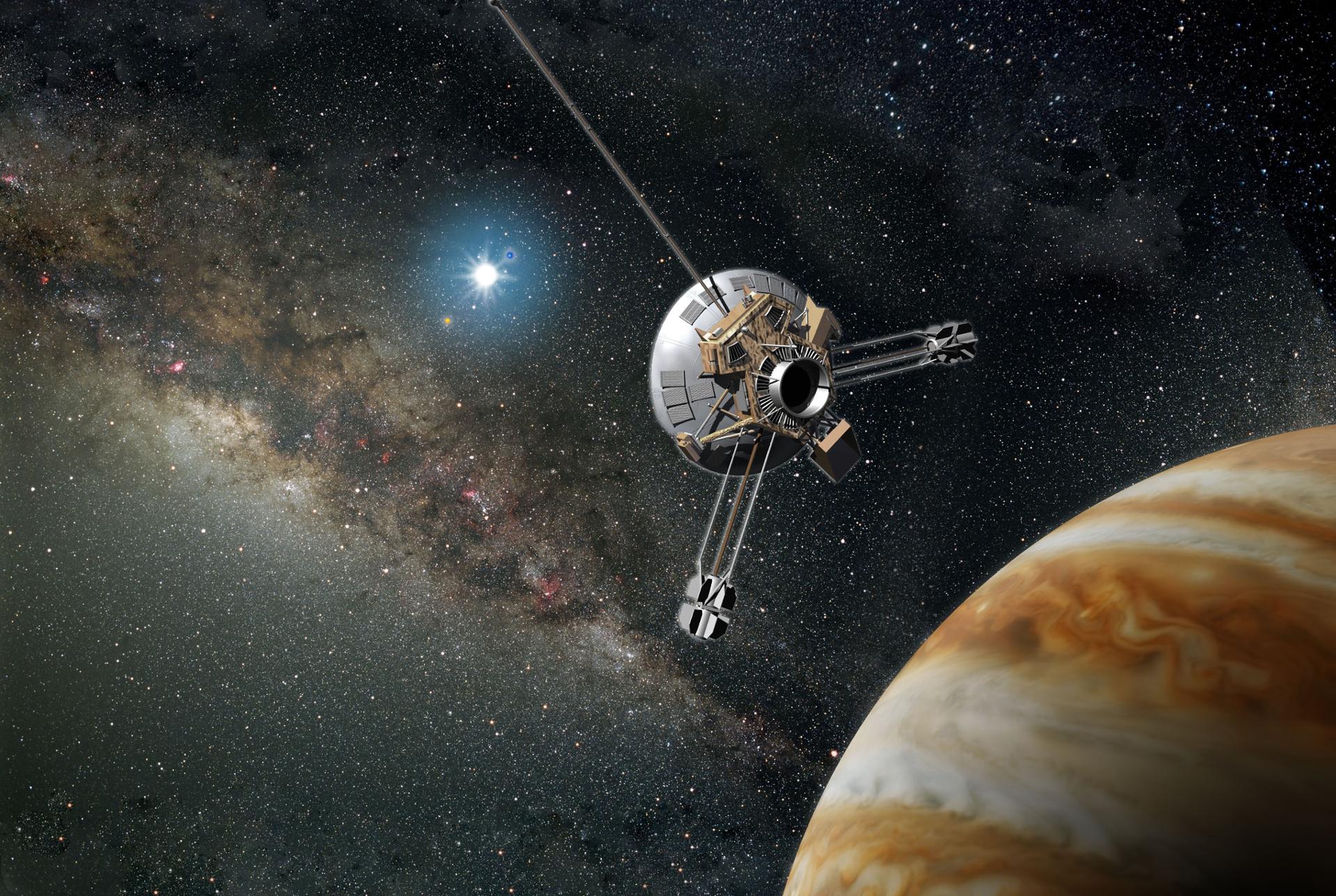
Pioneer
Launched on 2 March 1972, Pioneer 10 was the first spacecraft to travel through the Asteroid belt, and the first spacecraft to make direct observations and obtain close-up images of Jupiter. Famed as the most remote object ever made by man through most of its mission, Pioneer 10 is now over 8 billion miles away. (On 17 February 1998, Voyager 1's heliocentric radial distance equaled Pioneer 10 at 69.4 AU and thereafter exceeded Pioneer 10 at the rate of 1.02 AU per year.)Pioneer 10 made its closest encounter to Jupiter on 3 December 1973, passing within 81,000 miles of the cloudtops. This historic event marked humans' first approach to Jupiter and opened the way for exploration of the outer solar system
Click to watch animated footage of Pioneer!!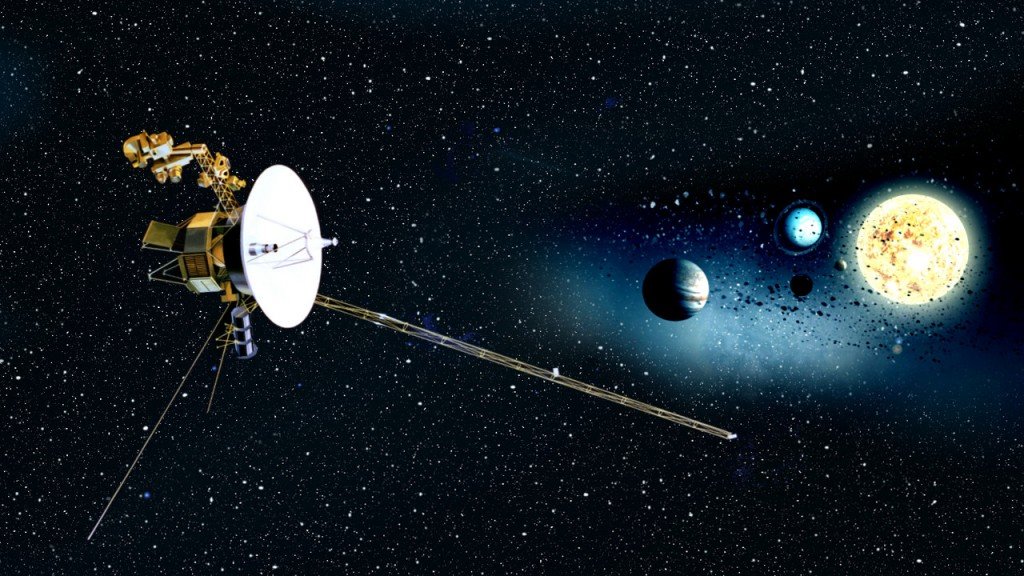
Voyager 1
Voyager 1 was constructed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It has 16 hydrazine thrusters, three-axis stabilization gyroscopes, and referencing instruments to keep the probe's radio antenna pointed toward Earth. Collectively, these instruments are part of the Attitude and Articulation Control Subsystem (AACS), along with redundant units of most instruments and 8 backup thrusters. The spacecraft also included 11 scientific instruments to study celestial objects such as planets as it travels through space.It is the first ever human made space craft to travel deep and interstellar space !! It has some proofs and data records about our earth which has been used to shake hands with any other civilization if contacted by Voyager 1
Click to watch Voyager's details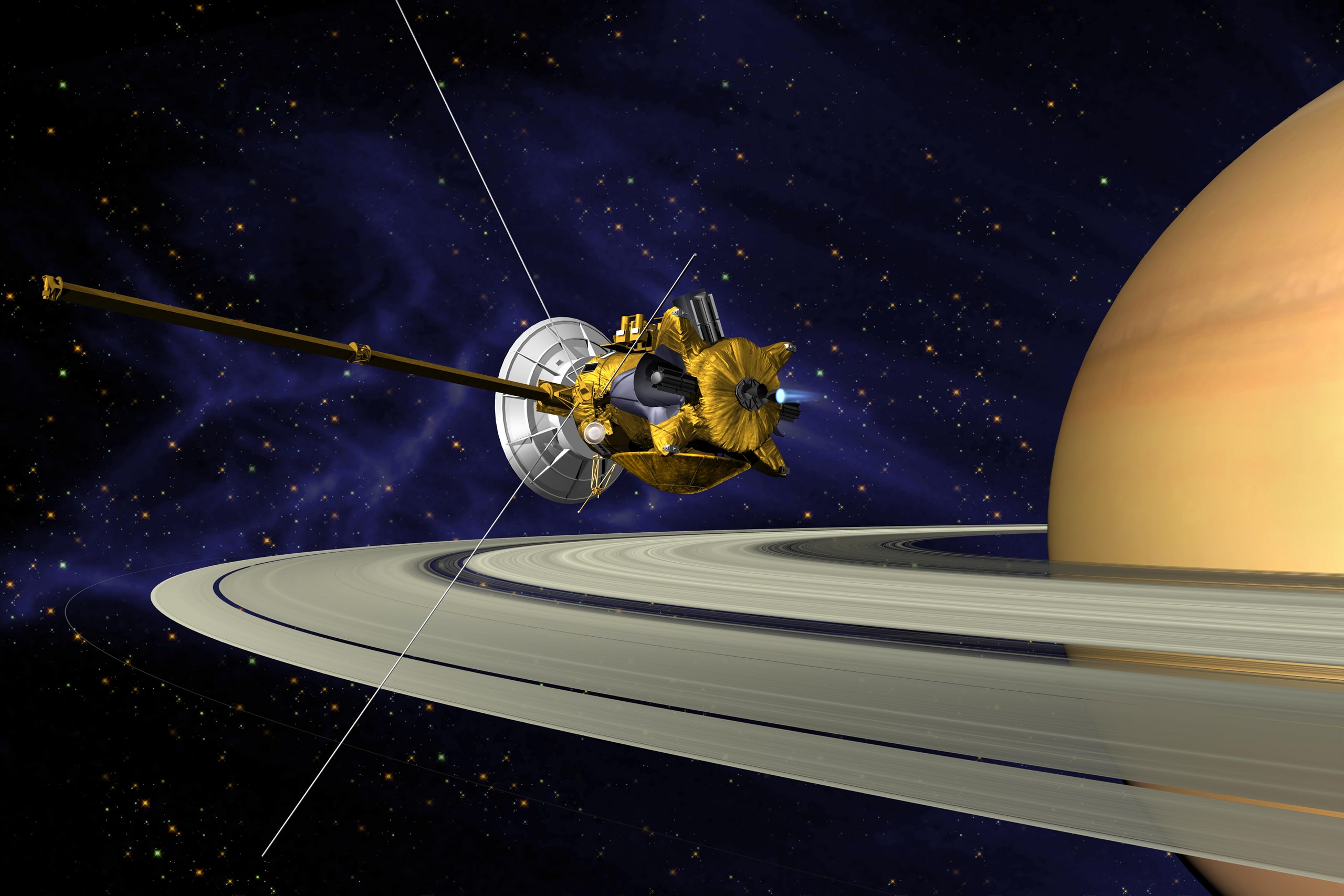
Cassini
The Cassini spacecraft orbited Saturn from June 30, 2004, until Sept. 15, 2017, when the probe ended its life with a plunge into the ringed planet's atmosphere. This intentional death dive was performed to make sure Cassini never contaminated a potentially habitable Saturn moon, such as Enceladus or Titan. [Cassini's Saturn Crash 2017: 'Grand Finale' at the Ringed Planet. The mission is known for discoveries such as finding jets of water erupting from Enceladus, and tracking down a few new moons for Saturn.
Click to watch the Cassini's Launch Click to watch Cassini's Grand Finale by Nasa, An incredible journey !!
Spitzer Space Telescope
Spitzer Space Telescope, U.S. satellite, the fourth and last of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration fleet of “Great Observatories” satellites. It studied the cosmos at infrared wavelengths. The Spitzer observatory began operating in 2003 and spent more than 16 years gathering information on the origin, evolution, and composition of planets and smaller bodies, stars, galaxies, and the universe as a whole. It was named in honour of Lyman Spitzer, Jr., an American astrophysicist who in a seminal 1946 paper foresaw the power of astronomical telescopes operating in space.
Click to watch the launching and description of Spitzer Telescope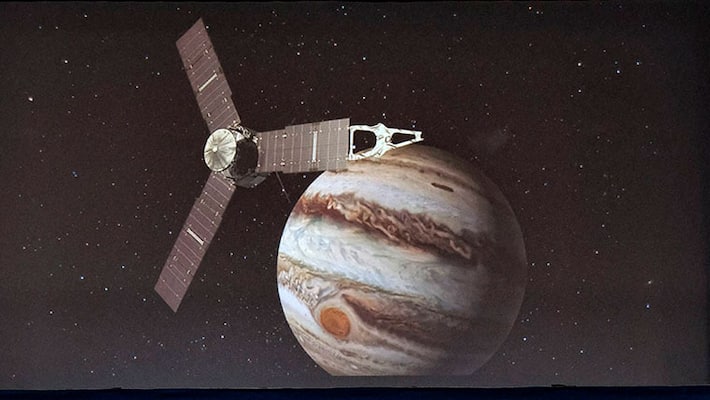
Juno
On August 5, 2011, NASA’s Juno spacecraft embarked on a 5-year journey to Jupiter, our solar system's largest planet. Juno arrived at Jupiter on July 4, 2016, after a five-year, 1,740-million-mile journey, and settled into a 53-day polar orbit stretching from just above Jupiter’s cloud tops to the outer reaches of the Jovian magnetosphere. During the prime mission’s 35 orbits of Jupiter, Juno collected more than three terabits of science data and provided dazzling views of Jupiter and its satellites, all processed by citizen scientists with NASA’s first-ever camera dedicated to public outreach. Juno’s many discoveries have changed our view of Jupiter’s atmosphere and interior, revealing an atmospheric weather layer that extends far beyond its water clouds and a deep interior with a dilute heavy element core. Near the end of the prime mission, as the spacecraft’s orbit evolved, flybys of the moon Ganymede initiated Juno’s transition into a full Jovian system explorer
Click to watch the launching of Juno!!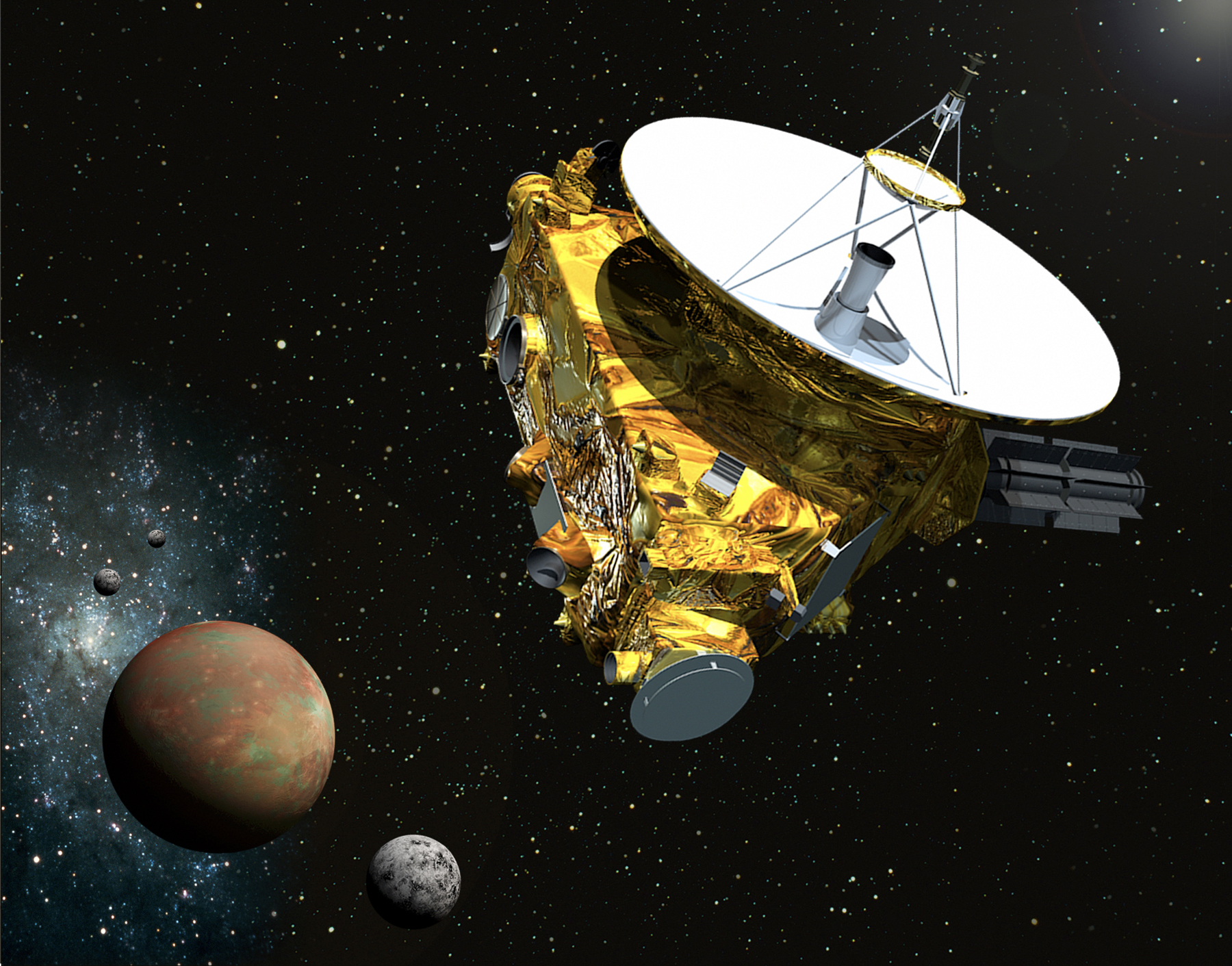
New Horizon
New Horizons is a NASA mission to study the dwarf planet Pluto, its moons, and other objects in the Kuiper Belt, a region of the solar system that extends from about 30 AU, near the orbit of Neptune, to about 50 AU from the Sun. It was the first mission in NASA’s New Frontiers program, a medium-class, competitively selected and principal investigator-led series of missions. (The program also includes Juno and OSIRIS-REx.)New Horizons was the first spacecraft to encounter Pluto, a relic from the formation of the solar system. By the time it reached the Pluto system, the spacecraft had traveled farther away and for a longer time period (more than nine years) than any previous deep space spacecraft ever launched. The design of the spacecraft was based on a lineage traced back to the CONTOUR and TIMED spacecraft, both also built by the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University. Besides its suite of scientific instruments.
Click to watch New Horizon's Documentary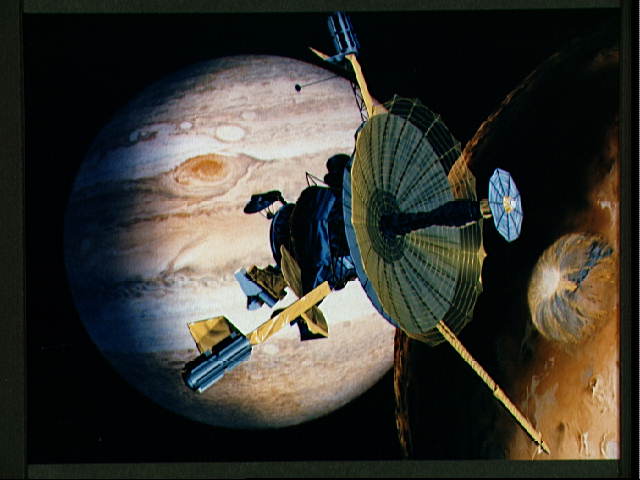
Galileo
While its aim was to study Jupiter and its mysterious moons, which it did with much success, NASA's Galileo mission also became notable for discoveries during its journey to the gas giant. It was the first spacecraft to visit an asteroid -- two in fact, Gaspra and Ida. Galileo provided the only direct observations of a comet colliding with a planet. And its flight past Venus in 1990 yielded fascinating infrared images of the planet's clouds.After discoveries including evidence for the existence of a saltwater ocean beneath the Jovian moon Europa's icy surface, extensive volcanic processes on the moon Io and a magnetic field generated by the moon Ganymede, Galileo plunged into Jupiter's atmosphere on September 21, 2003 to prevent an unwanted impact with Europa.
Click to watch Galileo's animated documentary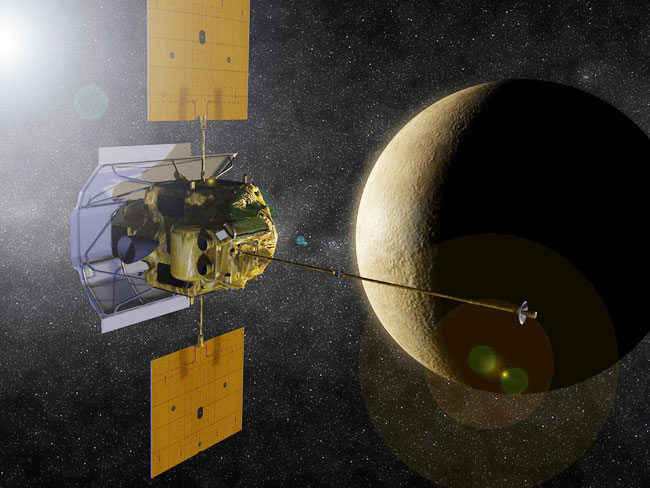
Messenger
MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) was the seventh Discovery-class mission, and the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury. Its primary goal was to study the geology, magnetic field, and chemical composition of the planet. It was the first mission to Mercury after Mariner 10, more than 30 years before. MESSENGER was launched at 06:15:57 UT Aug. 3, 2004, into an initial parking orbit around Earth. The six-and-a-half-year road to Mercury was punctuated by several gravity-assist maneuvers through the inner solar system, including one flyby of Earth (Aug. 2, 2005), two flybys of Venus (Oct. 24, 2006, and June 5, 2007), and three flybys of Mercury (Jan. 14, 2008, Oct. 6, 2008, and Sept. 29, 2009).
Click to watch Messenger's Documentary and details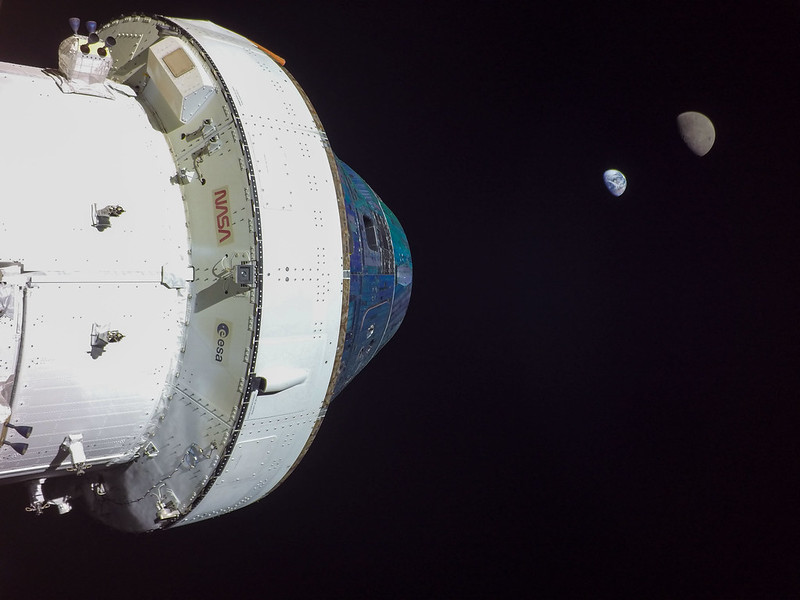
Artemis 1
Formerly called Exploration Mission-1, this uncrewed mission took place in November-December 2022, and was an extensive test of the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion module. Artemis 1's journey took it 450,000 km to the Moon, where it orbited 130 km above the lunar surface, before continuing approximately 64,373 km beyond into deep space. After a mission length of 25.5 days, the module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean near California on 11 December.On board were a range of science and technology experiments that took place in deep space. These were designed to expand lunar knowledge, make further technological developments, and shed light on deep space radiation. Also on board were three 'Moonikins': mannequins wearing the First-Generation Orion Crew Survival System spacesuit which the real astronauts will wear on Artemis 2 and 3. Sensors on the Moonikins provided crucial data on what human crew members may experience during flight.
Click to watch Artemis 1 Launch!!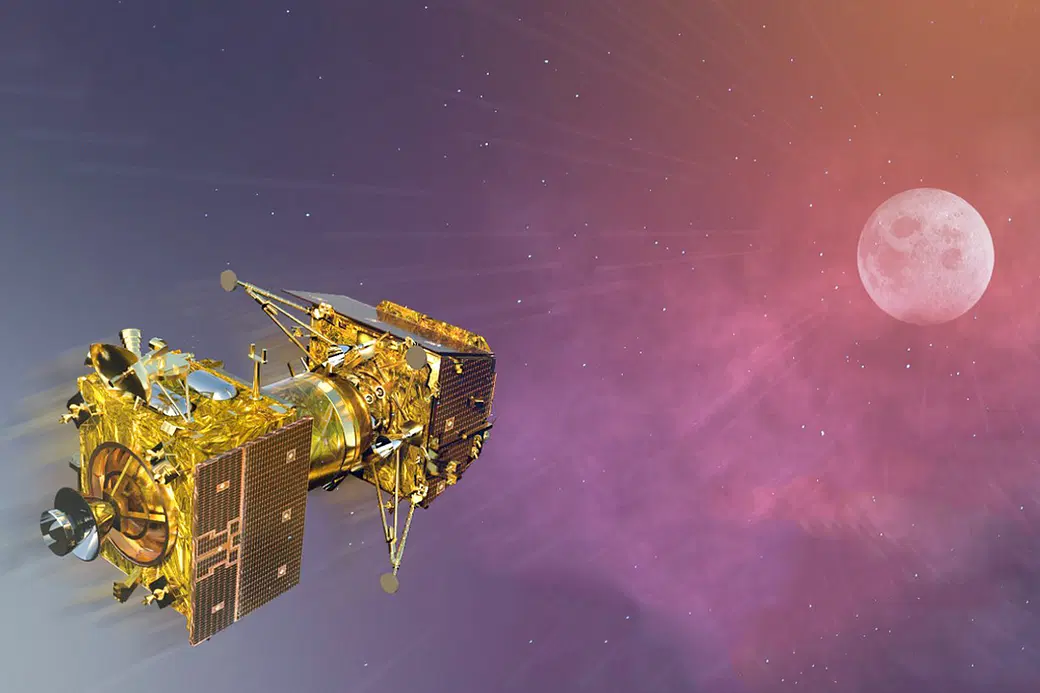
Chandrayaan 3
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It consists of Lander and Rover configuration. It will be launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit. The propulsion module has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit. Lander payloads: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature; Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) for measuring the seismicity around the landing site; Langmuir Probe (LP) to estimate the plasma density and its variations. Rover payloads: Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) for deriving the elemental composition in the vicinity of landing site.
Click to watch Chandrayaan 3 Launch!!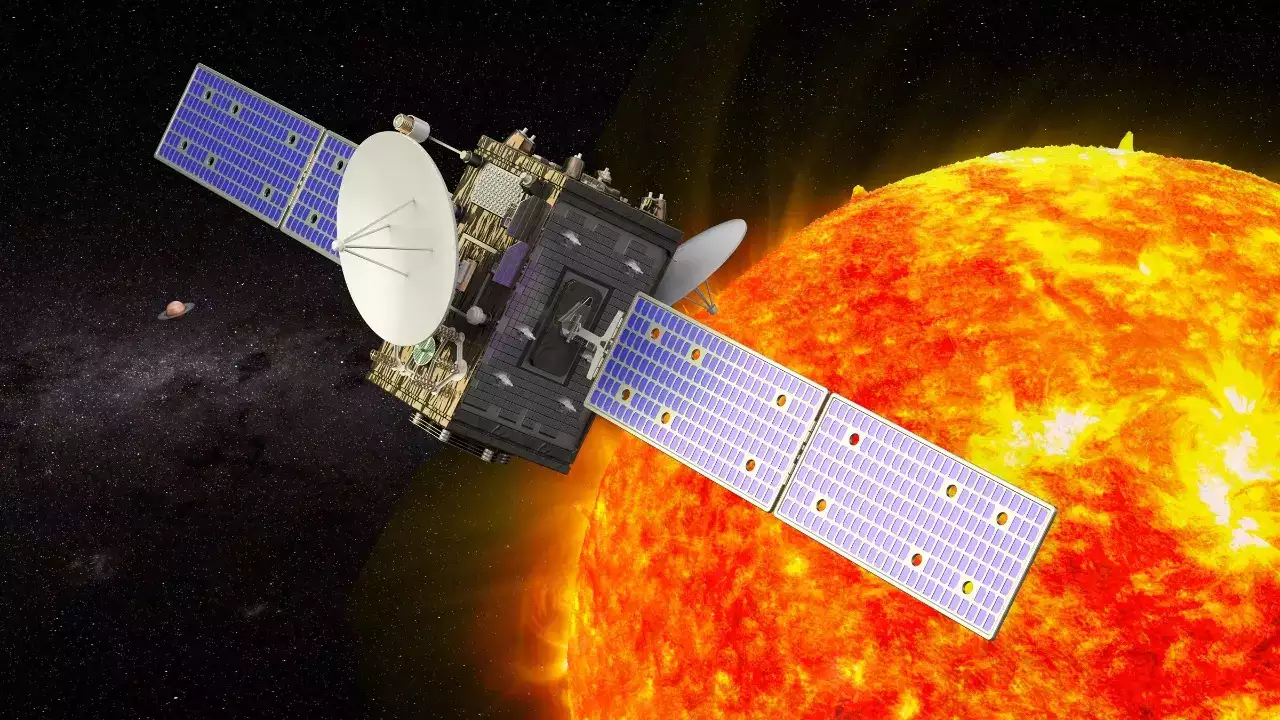
Aditya L1
Aditya-L1, India's first dedicated solar space mission, is named after the Sun God and is set to revolutionize our understanding of the Sun and its impact on space weather. The primary objective of the mission is to study the Sun's corona, chromosphere, and photosphere, shedding light on fundamental solar processes and their effects on Earth. Equipped with a suite of instruments designed to observe the Sun in various wavelengths, Aditya-L1 will provide invaluable data on solar dynamics, magnetic fields, and eruptive events like solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Scheduled for launch, Aditya-L1 promises to deepen our knowledge of the Sun-Earth connection and pave the way for advancements in space weather forecasting and solar physics research.
Click to watch Aditya L1 launch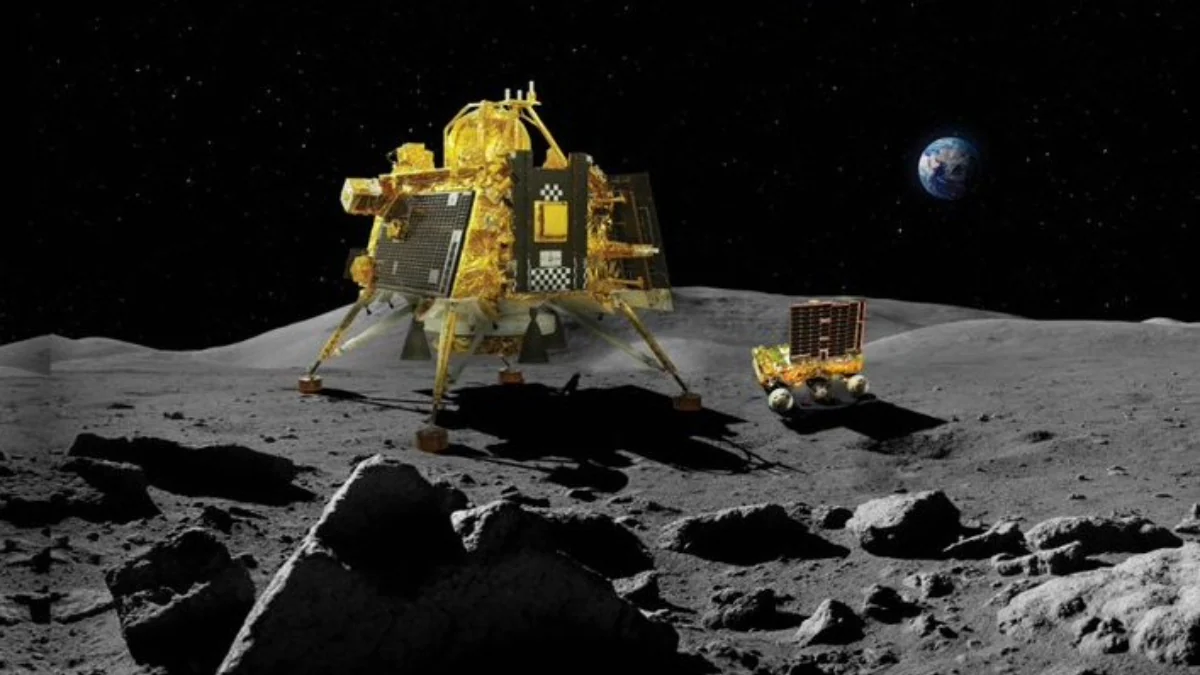
Japan's SLIM probe
Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon) probe represents the nation's ambitious endeavor to explore the lunar surface with precision and sophistication. SLIM is designed to land autonomously on the Moon, employing advanced navigation and guidance systems to ensure pinpoint accuracy. Equipped with a suite of scientific instruments, including cameras and spectrometers, SLIM aims to conduct detailed investigations of the lunar terrain, composition, and geology. By studying the Moon's surface features and geological history, SLIM seeks to unravel mysteries about the Moon's formation and evolution, offering insights into the early history of our solar system. With its innovative technology and scientific objectives.
Click to watch Japan's SLIM probe launchHumans have played a central role in shaping the understanding of the universe through scientific observation and experiment. Physical cosmology was shaped through both mathematics and observation in an analysis of the whole universe.The universe is generally understood to have begun with the Big Bang, followed almost instantaneously by cosmic inflation, an expansion of space from which the universe is thought to have emerged 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years ago.Cosmogony studies the origin of the Universe, and cosmography maps the features of the Universe. In Diderot's Encyclopédie, cosmology is broken down into uranology (the science of the heavens), aerology (the science of the air), geology (the science of the continents), and hydrology (the science of waters).Metaphysical cosmology has also been described as the placing of humans in the universe in relationship to all other entities. This is exemplified by Marcus Aurelius's observation that a man's place in that relationship: "He who does not know what the world is does not know where he is, and he who does not know for what purpose the world exists, does not know who he is, nor what the world is."